
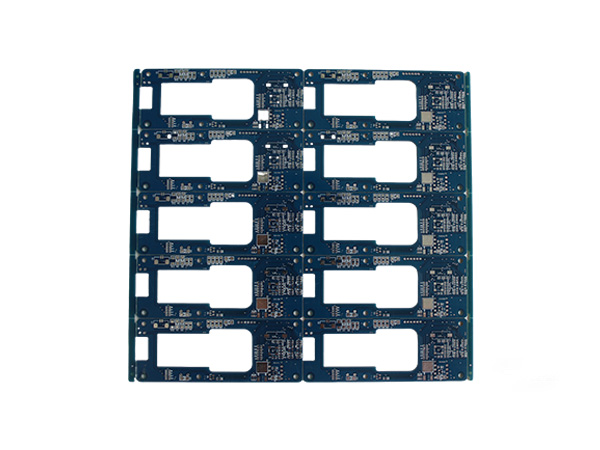
HDI PCBs
Rigid-Flex PCB
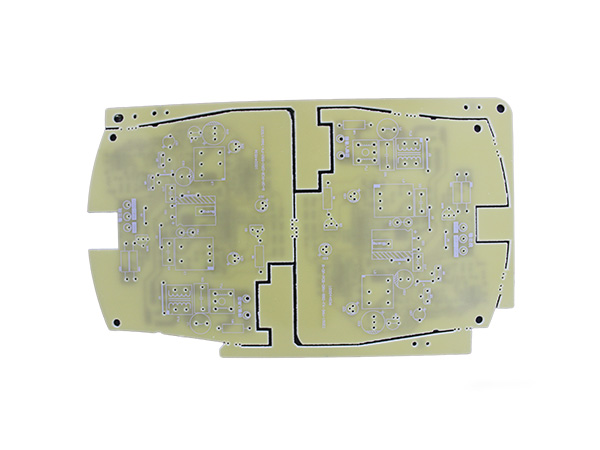
RF and high speed PCB
Glass Substrate
IC Substrate
Ceramic PCB
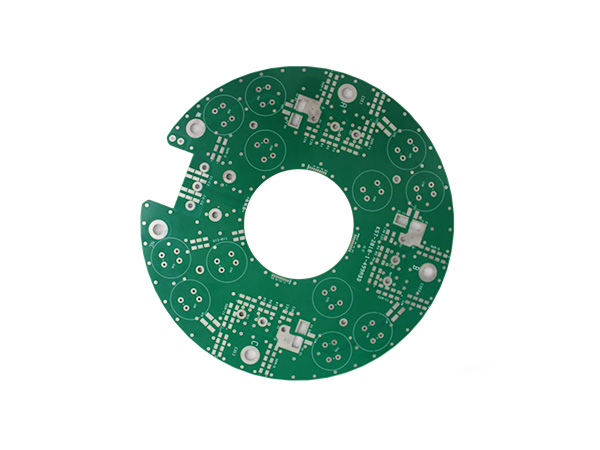
Metal-Core & Metal-Clad PCBs
Ultrathin PCB
High-Speed & RF/Microwave PCBs
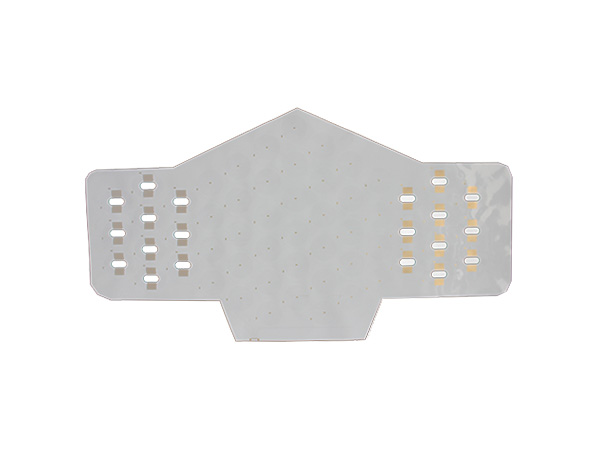
Material: IT180 TG180 FR4
Thickness: 1.60mm
Layer: 6L
Copper: 35um
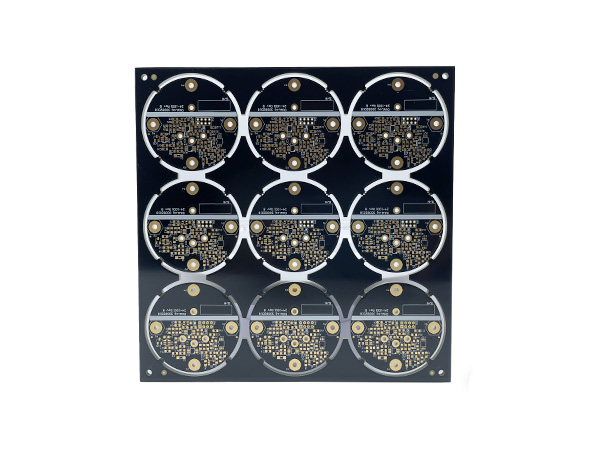

Material: IT180 TG180 FR4
Thickness: 1.60mm
Layer: 6L
Copper: 35um
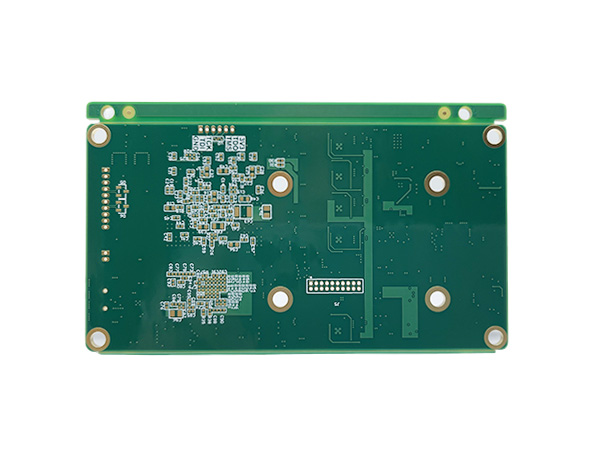
Material: IT180 TG180 FR4
Thickness: 1.60mm
Layer: 6L
Copper: 35um
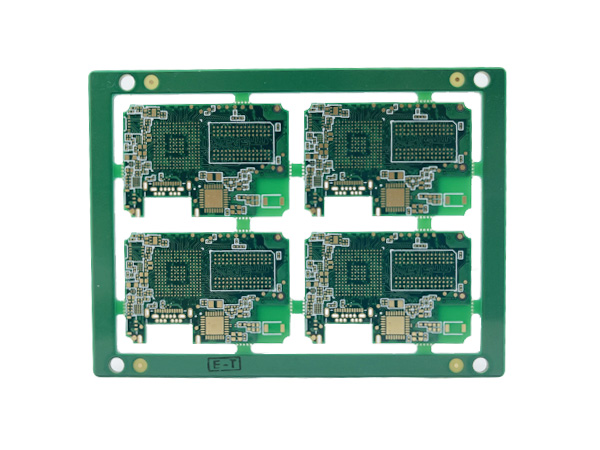
Material: IT180 TG180 FR4
Thickness: 1.60mm
Layer: 6L
Copper: 35um
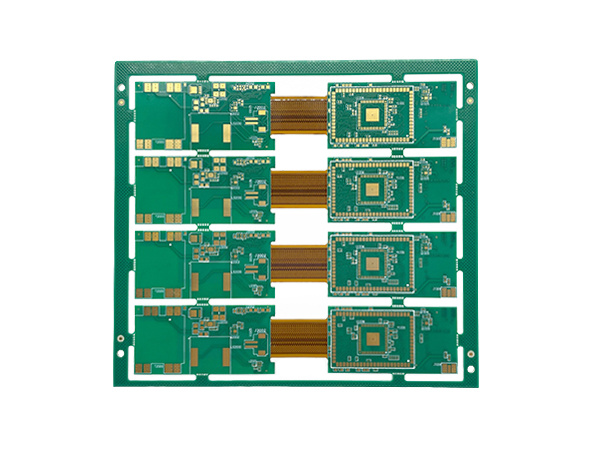
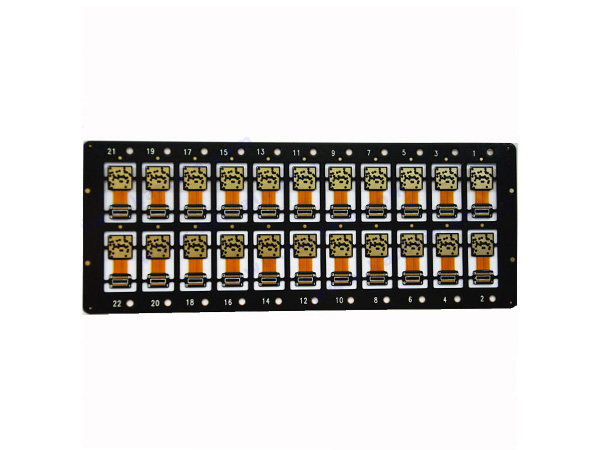
Name:communication devide flex rigid pcb Material: IT180 TG180 FR4 Thickness:1.60mm Layer:6L Copper:35um
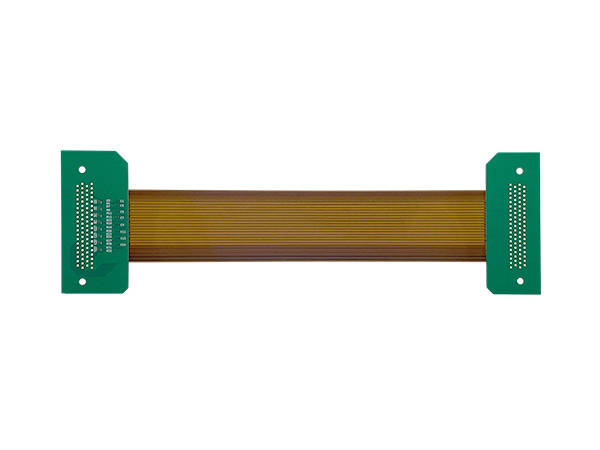
Name:Flat cable flex rigid pcb Material: IT180 TG180 FR4 Thickness:1.60mm Layer:6L Copper:35um

Designed specifically for camera modules, it features a 4-layer flexible circuit structure and supports the transmission of signals from high-resolution sensors and multiple lenses.

Chip-on-FPC technology, where the driving IC is directly bonded to the flexible circuit board, enabling ultra-narrow bezel display.
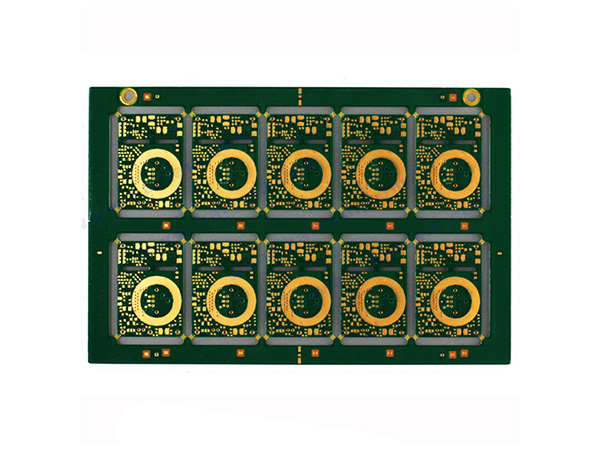
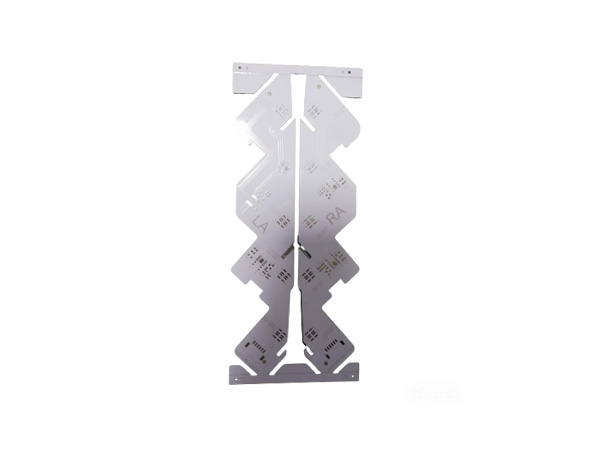
This is a 4-layer circuit board based on FR4 rigid substrate, which achieves high-density interconnection through the blind hole/mounted hole technology.
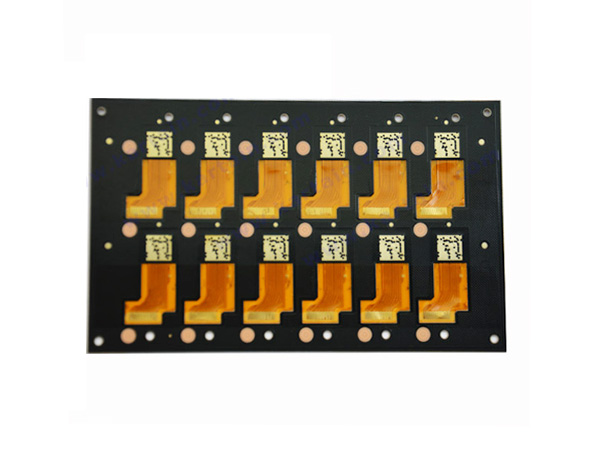
Utilizing chemical nickel-palladium-gold (ENEPIG) surface treatment to enhance the reliability and corrosion resistance of FPC welding.
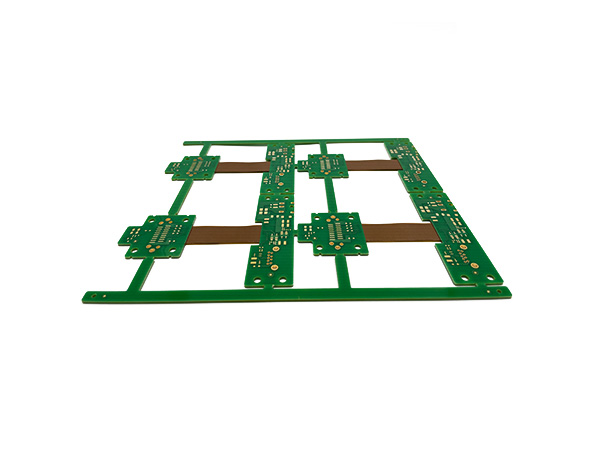
Rigid-Flex PCB (Rigid-Flex Circuit Board) is a hybrid type of circuit board that combines a rigid circuit board (Rigid PCB) with a flexible circuit board (Flex PCB) through a special process. Its core design concept is to integrate the mechanical stability of the rigid area and the bending adaptability of the flexible area on a single board, and achieve three-dimensional wiring through interlayer transitions to meet the strict requirements of complex electronic devices for space, weight, and reliability.
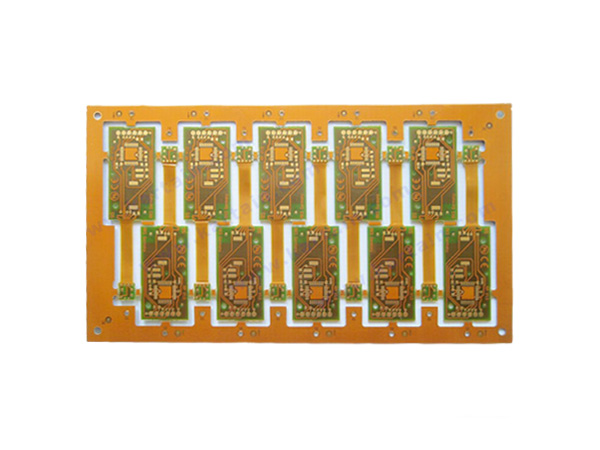
The 6-layer FPC is a flexible circuit board constructed by alternating six layers of conductive copper layers with flexible dielectric materials (such as polyimide). Its core advantages lie in high-density wiring, lightweight design, and excellent bending performance. It is widely used in fields with strict requirements for space, weight, and reliability, such as smart phones, wearable devices, medical electronics, and aerospace.

The copper conductive plate is a plate-shaped conductive material made of high-purity copper or copper alloy as the base material. Due to its excellent physical and chemical properties, it is widely used in the fields of electrical engineering, electronics, energy, and construction.
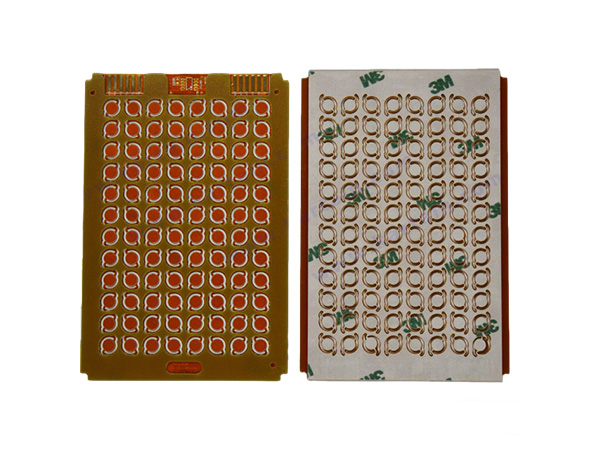

The double-layer flexible circuit board (2-Layer FPC) is composed of two layers of conductive copper foil and a flexible substrate (such as polyimide or polyester film).
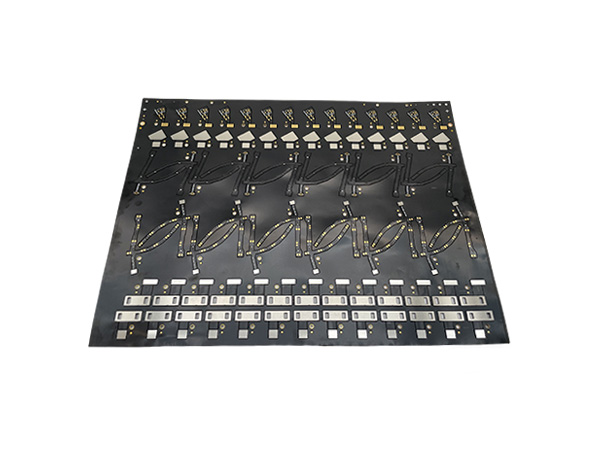
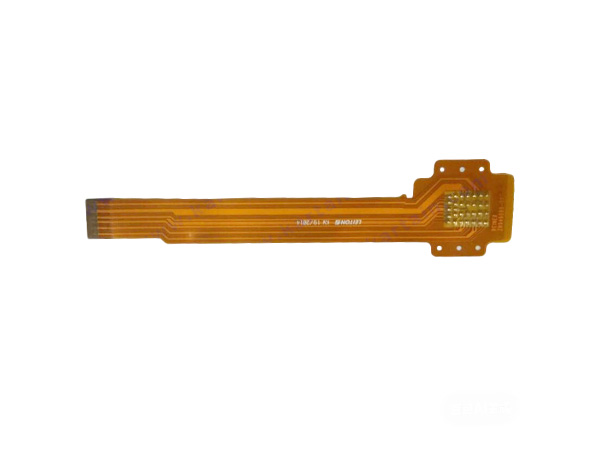
Flexible Printed Circuit Board (FPC) is a type of circuit board that uses flexible substrates (such as polyimide, polyester film, etc.) as its core. It is manufactured through printing technology to create conductive circuits and can integrate electronic components.
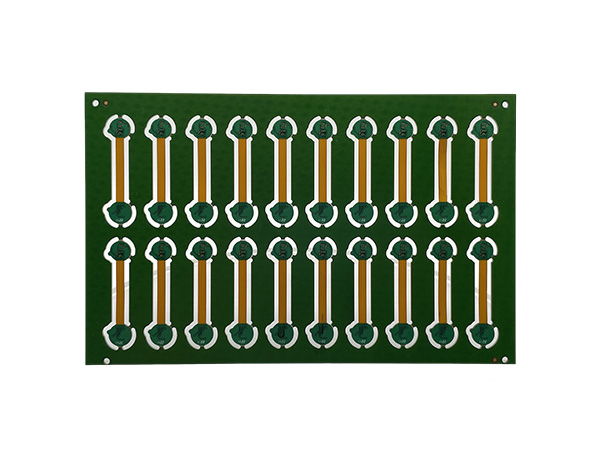
Flexible Printed Circuit Board (FPC) is a type of circuit board that uses flexible substrates (such as polyimide, polyester film, etc.) as its core. It is manufactured through printing technology to create conductive circuits and can integrate electronic components.
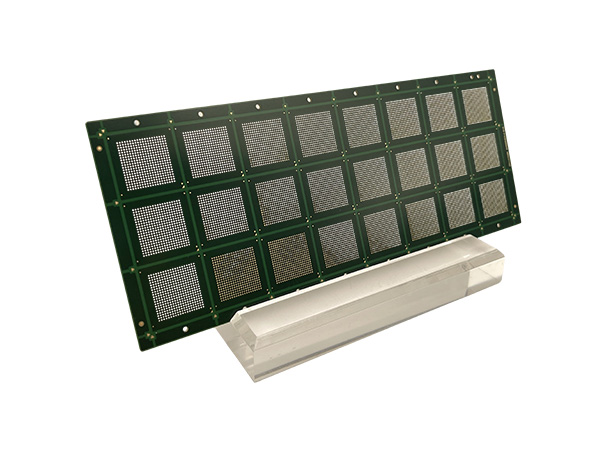
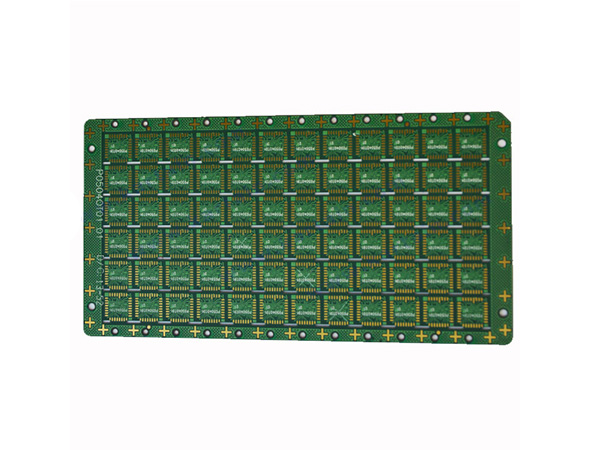
IC Substrate, also known as Integrated Circuit Substrate, is the core component of chip packaging, located between the bare chip (Bare Die) and the main PCB (Motherboard).
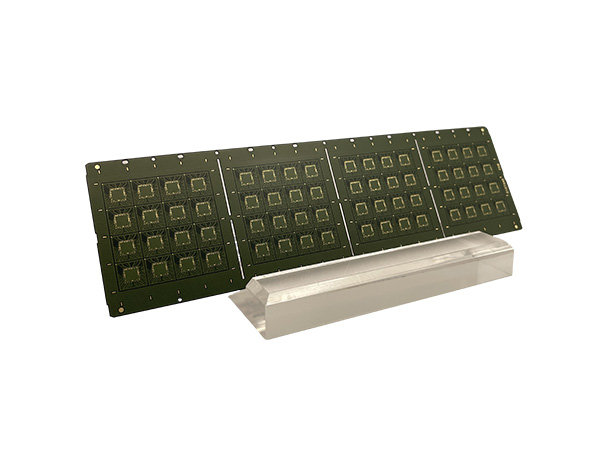

IC Substrate, also known as Integrated Circuit Substrate, is the core component of chip packaging, located between the bare chip (Bare Die) and the main PCB (Motherboard).
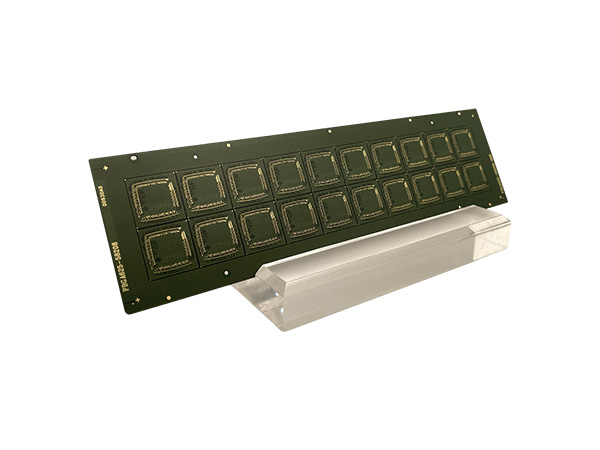

IC Substrate, also known as Integrated Circuit Substrate, is the core component of chip packaging, located between the bare chip (Bare Die) and the main PCB (Motherboard).
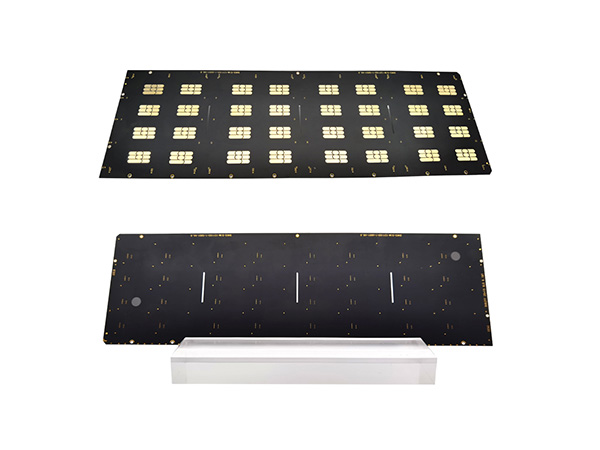

IC Substrate, also known as Integrated Circuit Substrate, is the core component of chip packaging, located between the bare chip (Bare Die) and the main PCB (Motherboard).

IC Substrate, also known as Integrated Circuit Substrate, is the core component of chip packaging, located between the bare chip (Bare Die) and the main PCB (Motherboard).
IC Substrate, also known as Integrated Circuit Substrate, is the core component of chip packaging, located between the bare chip (Bare Die) and the main PCB (Motherboard).

IC Substrate, also known as Integrated Circuit Substrate, is the core component of chip packaging, located between the bare chip (Bare Die) and the main PCB (Motherboard).
Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.

Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.
Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.

Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.

Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.
Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.

Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.

Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.
Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.

Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.

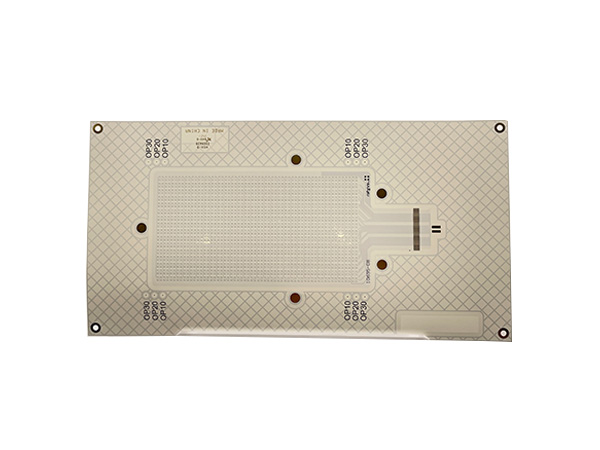
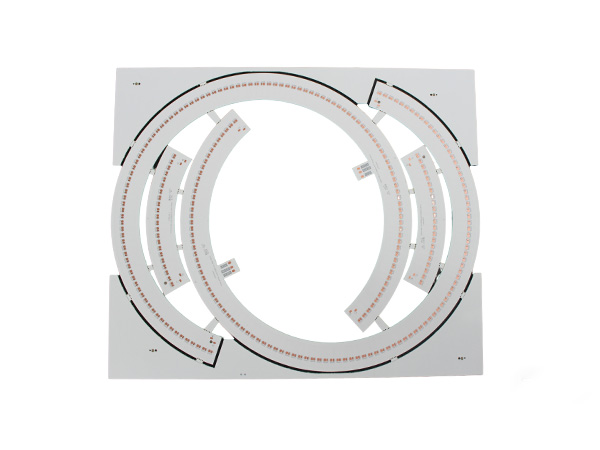
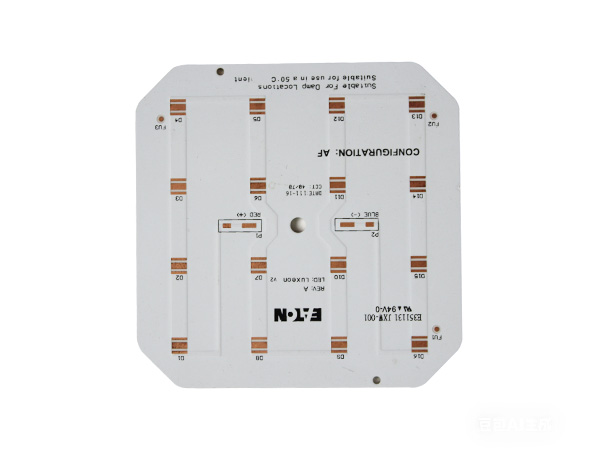
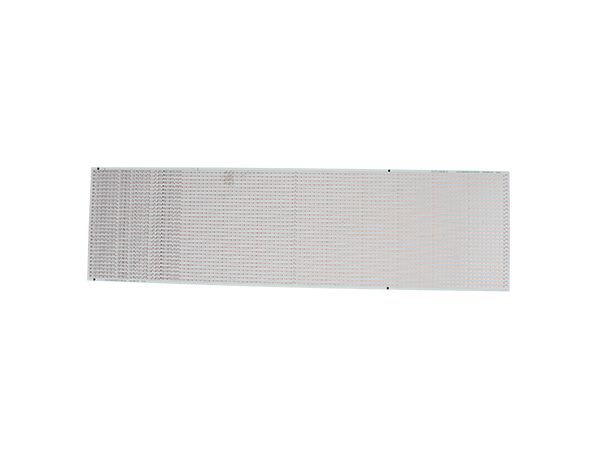
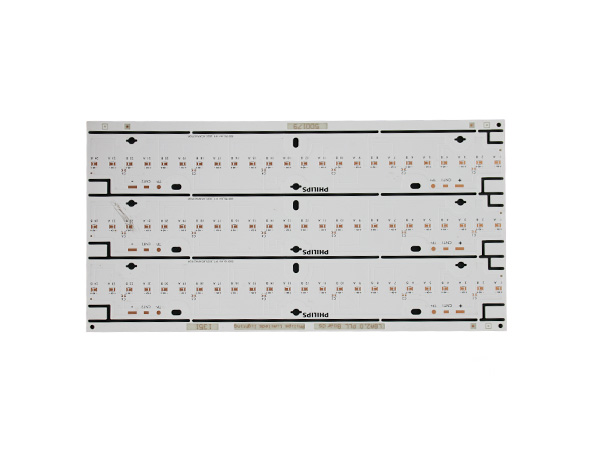
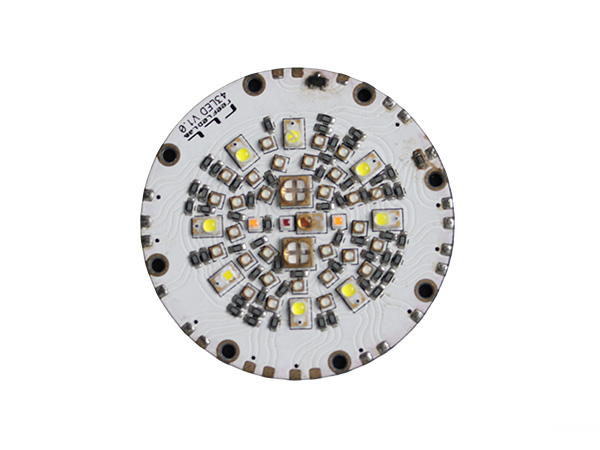
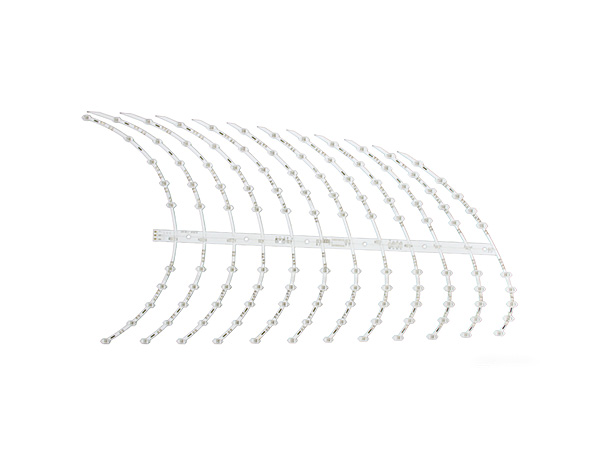
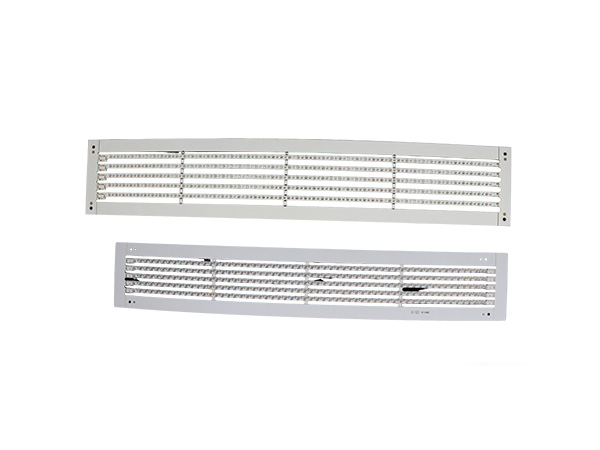
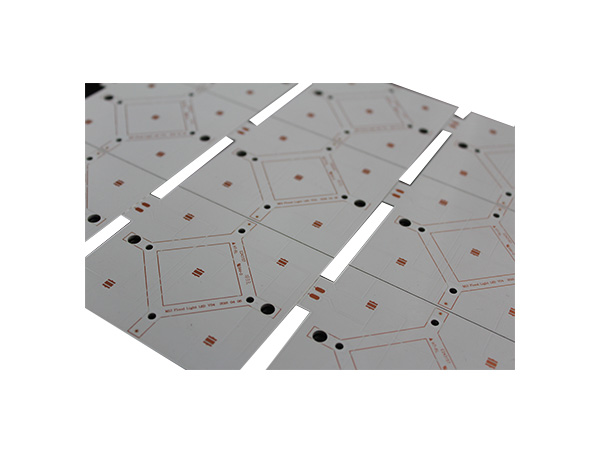
High-power LED PCB boards are circuit boards specifically designed for high-power LED lighting systems. Their core function is to ensure the stable operation of LEDs under power ranging from tens to hundreds of watts by optimizing the heat dissipation structure and electrical layout. These circuit boards integrate heat-dissipating substrates, thermal conductive medium layers, and electrical circuits, efficiently conducting the heat generated by the LED chips to the external environment while maintaining the stable transmission of electrical signals. As a result, they extend the lifespan of LEDs and enhance the luminous efficiency.
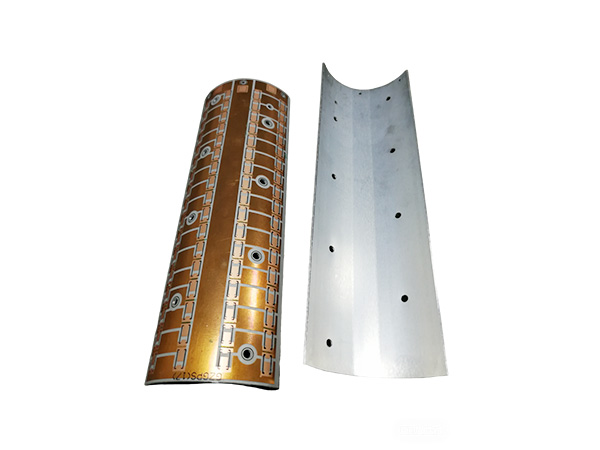

Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.

Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.

Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.

Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.

Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.
Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.

Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.
Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.
Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.
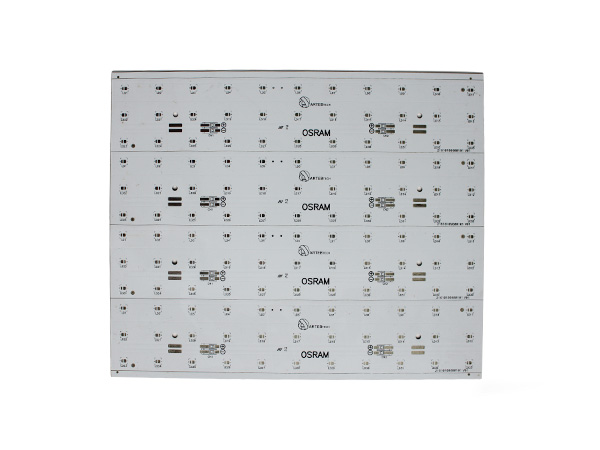
Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.
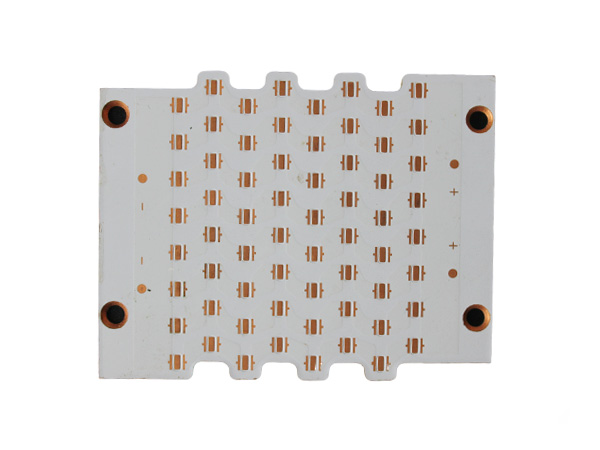
Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.
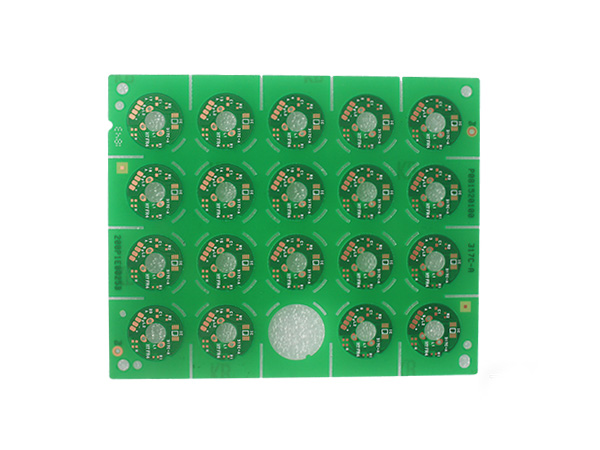
Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.

The flexible circuit board of the printer is the specific application of flexible printed circuit (Flexible Printed Circuit, abbreviated as FPC) in printer equipment. FPC uses flexible materials such as polyester film or polyimide (PI) as the base material, and through etching technology, forms single-sided, double-sided or multi-layer circuit boards on the surface.
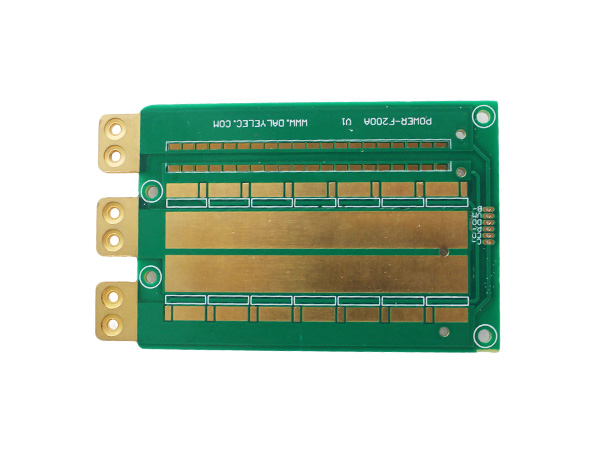
Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.
Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.

Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.

Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.
Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.
Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.

Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.
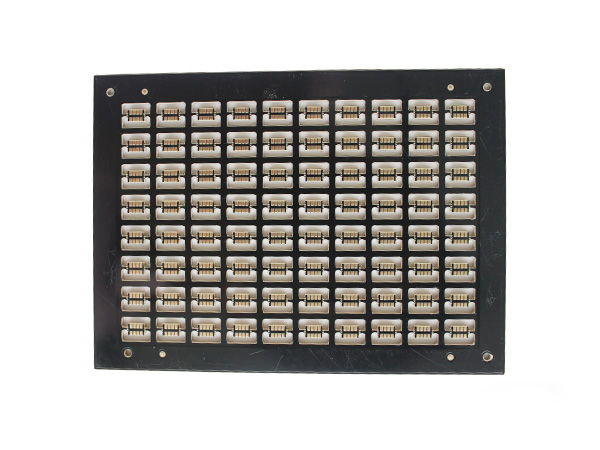

Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.
Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.
Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.
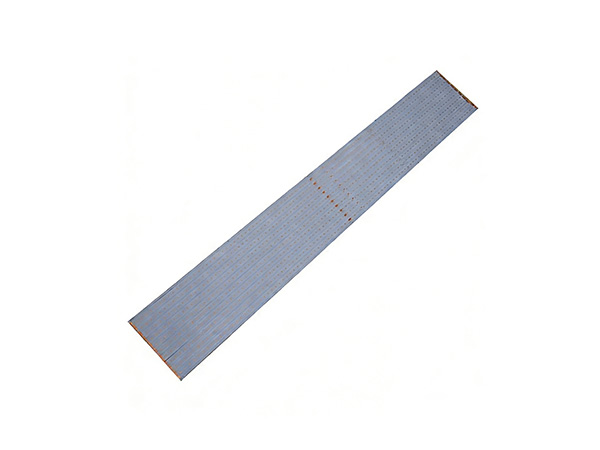

FR4 LED PCB Boards are printed circuit boards manufactured using FR4 substrate (glass fiber reinforced epoxy resin laminate). They are specifically designed for LED lighting applications. Due to their excellent electrical insulation, mechanical strength, heat resistance, and cost-effectiveness, FR4 has become the mainstream substrate choice in the LED lighting field.
Metal-clad PCBs (MCPCBs) are printed circuit boards with metal (such as aluminum or copper) as the core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "metal substrate + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + copper foil circuit layer", they achieve a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and are widely used in high-power density electronic devices.
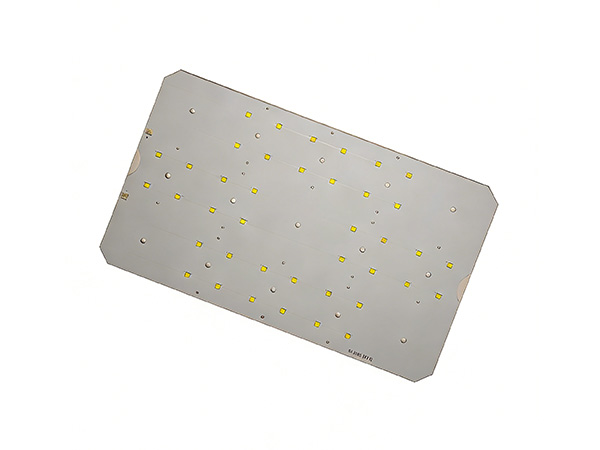

Material:Aluminum
Layer:1layer
Board Thickness:2.0mm
Surface finished:HASL
Soldermask:White color
Application:High quality LED streed light
LED source:40pcs CREE XP-L LED
Color Temperature:6000-6500K cool white
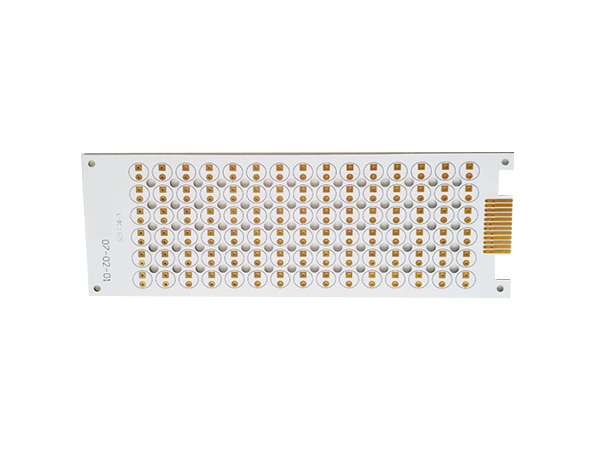

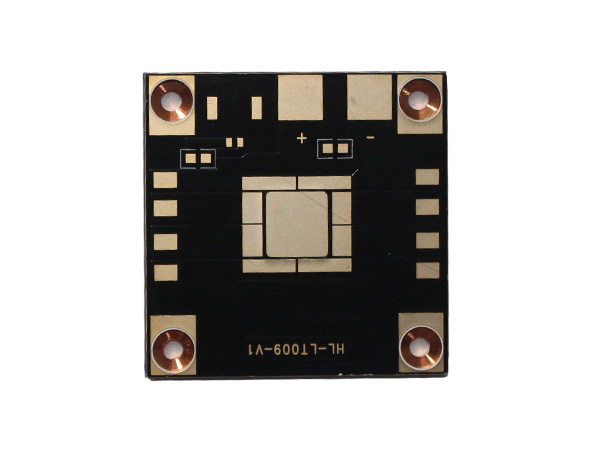
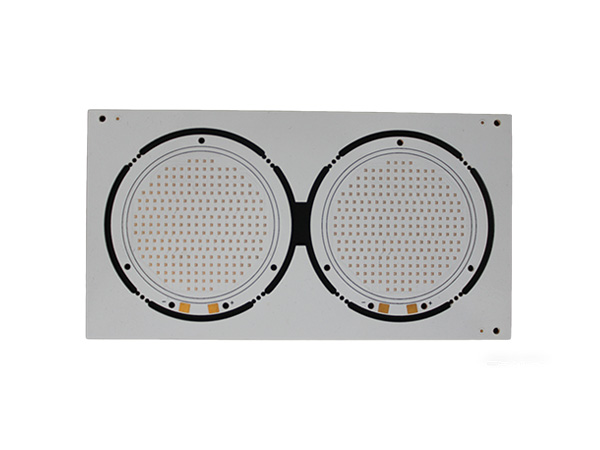
2 Layer Aluminum PCB is a high-performance metal-based printed circuit board (MCPCB), specifically designed for applications that require efficient heat dissipation and mechanical strength. By combining double-layer copper foil circuits with an aluminum substrate, it achieves a dual optimization of electrical performance and thermal management. It is widely used in fields such as LED lighting, power modules, automotive electronics, and industrial control.
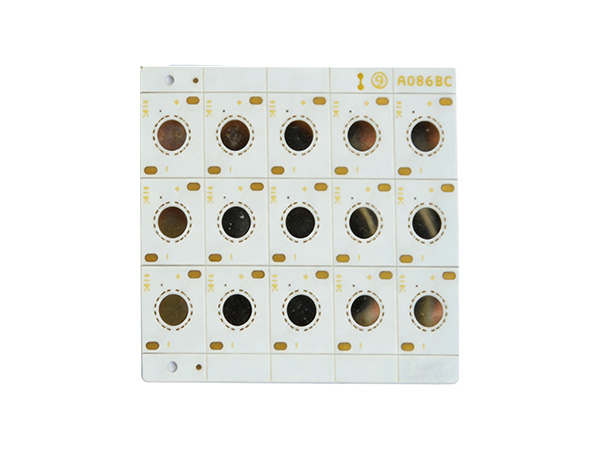

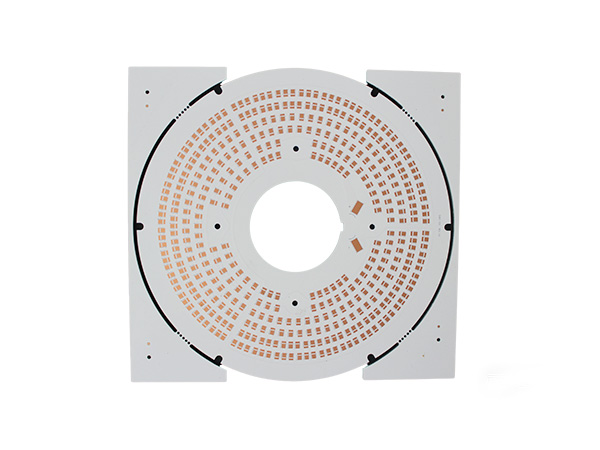
COB Aluminum PCB Board is a high-performance circuit board that combines the chip-on-board (COB) technology with aluminum-based printed circuit boards. It is specifically designed for applications with high power density and high heat dissipation requirements. It achieves electrical connection by directly fixing bare chips (Die) on the aluminum substrate and using gold wires or aluminum wires for bonding.
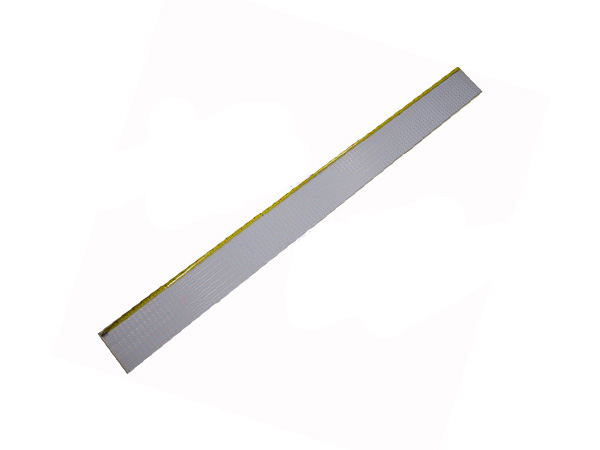

A 1.5mm-thick aluminum-based printed circuit board (Aluminum PCB) is a special type of circuit board with metal aluminum as its core substrate. Through a sandwich structure of "copper foil circuit layer + high thermal conductivity insulating layer + aluminum metal substrate", it achieves a balance of efficient heat dissipation, high mechanical strength and electrical insulation, and is widely used in high-power density electronic devices.

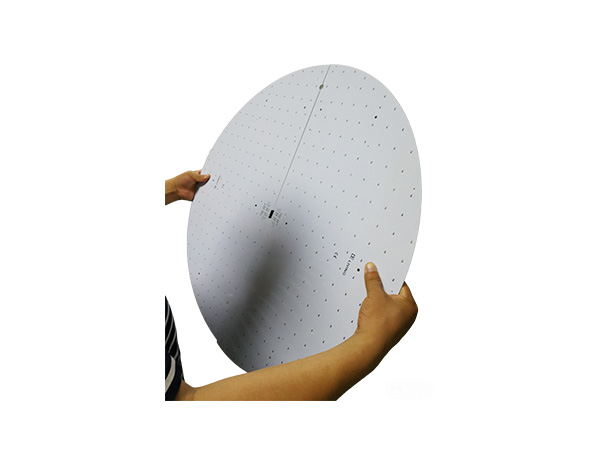
Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.
Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.
Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.
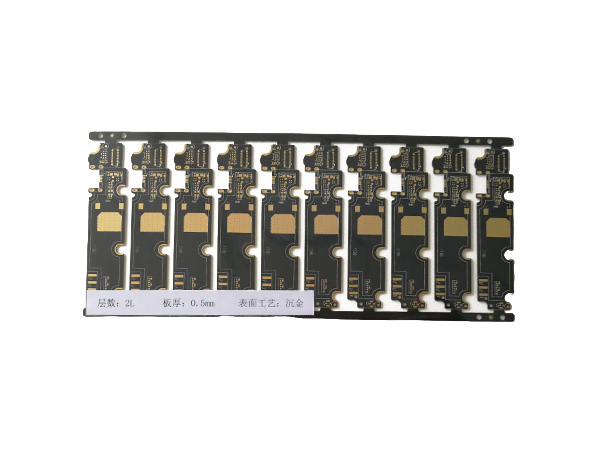

Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.
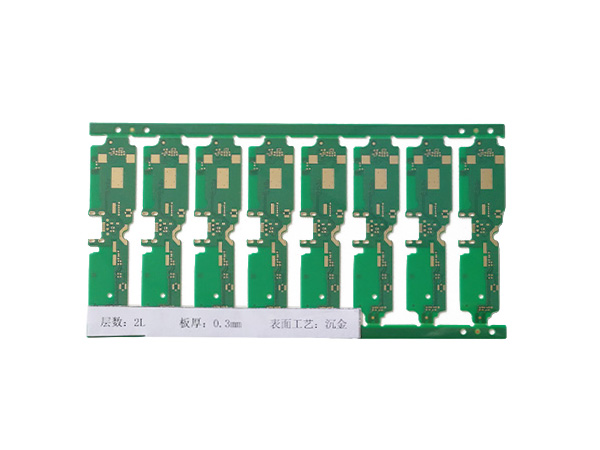
Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.
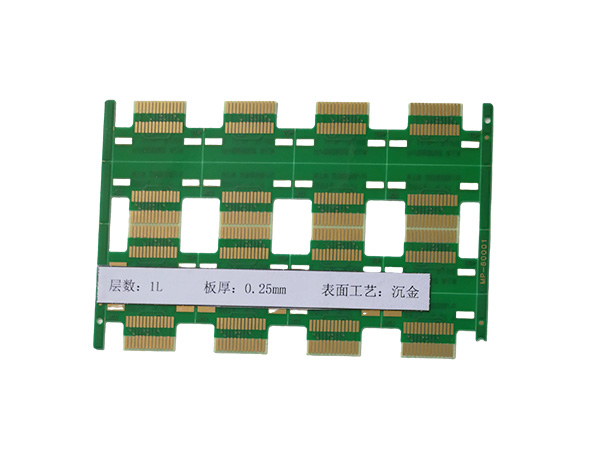

Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.
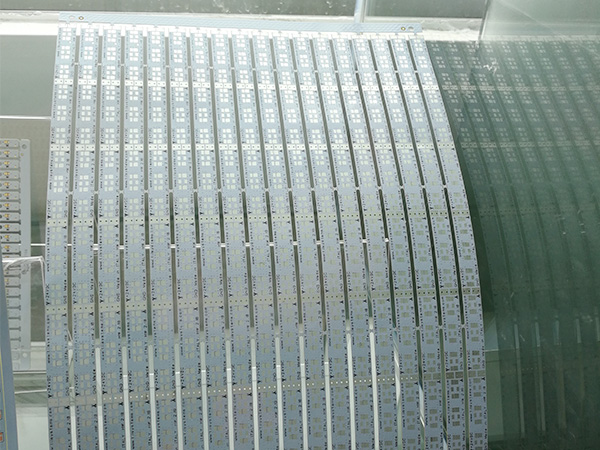

Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.
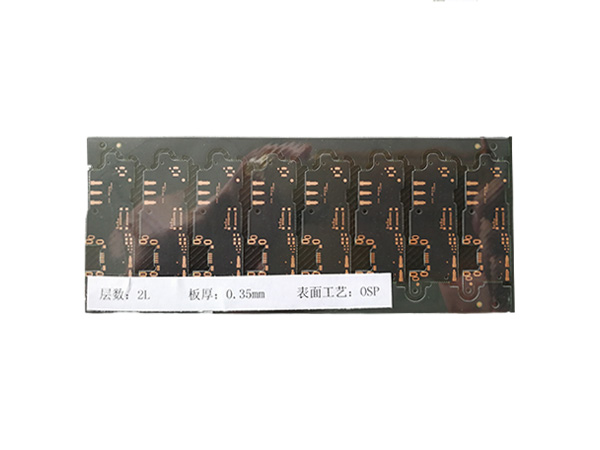

Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.

Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.

Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.
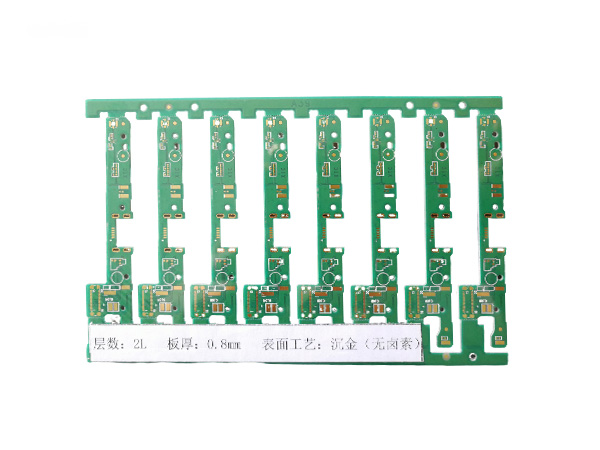
Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.
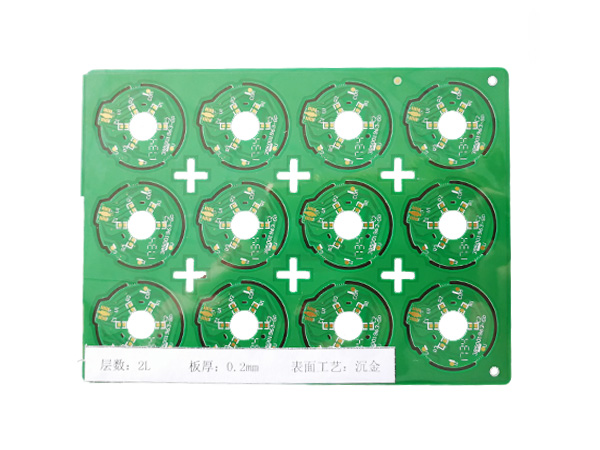
Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.
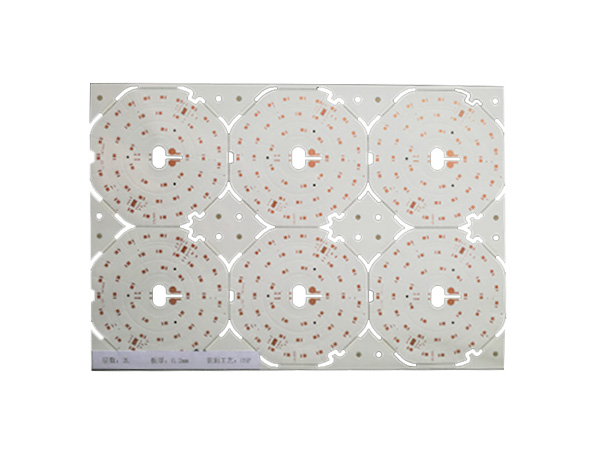

Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.
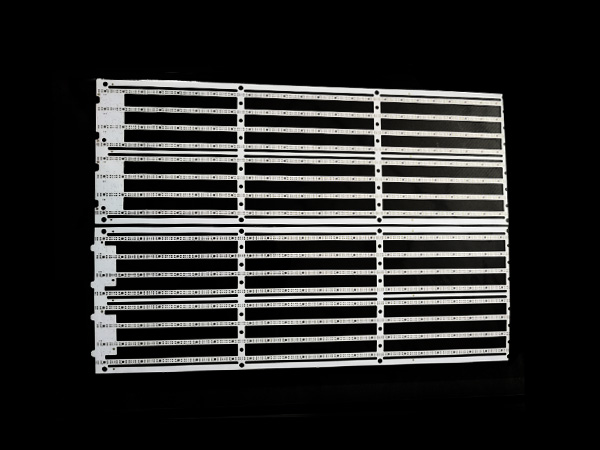
Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.
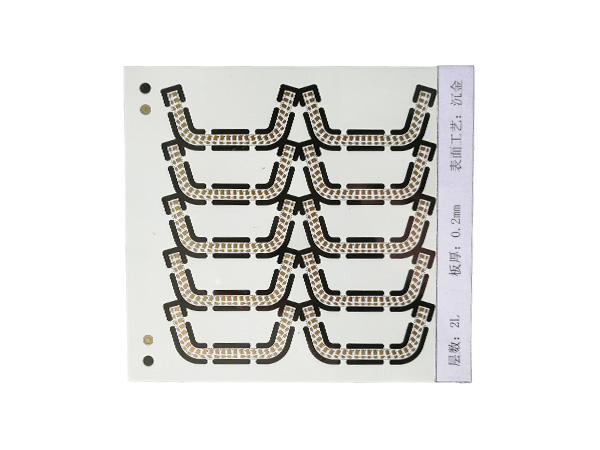
Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.
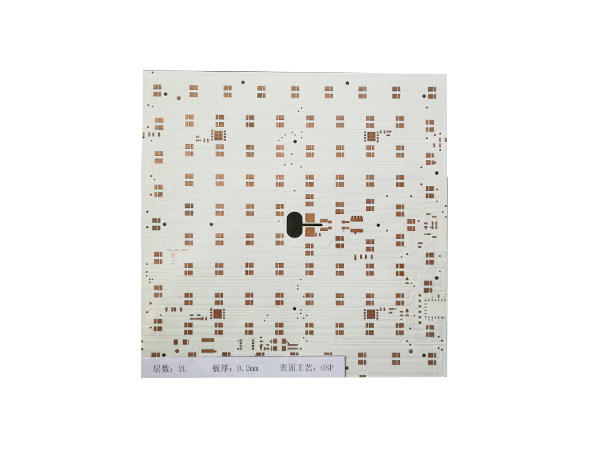
Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.
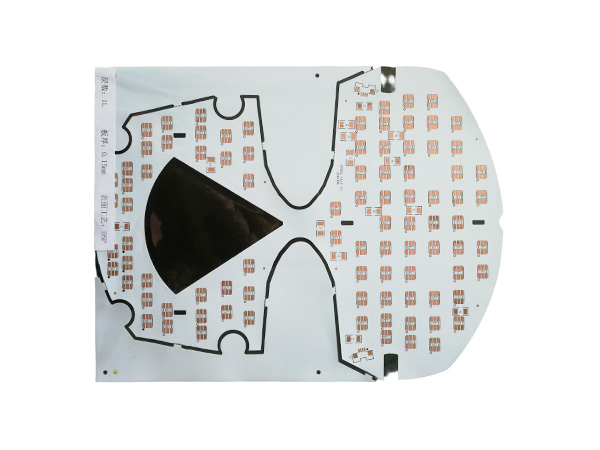
Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.
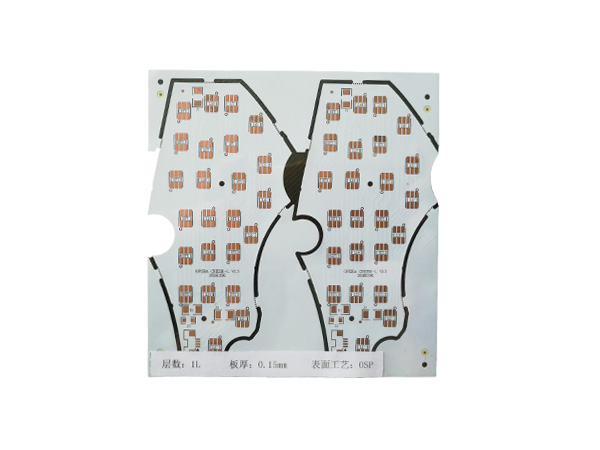
Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.

Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.
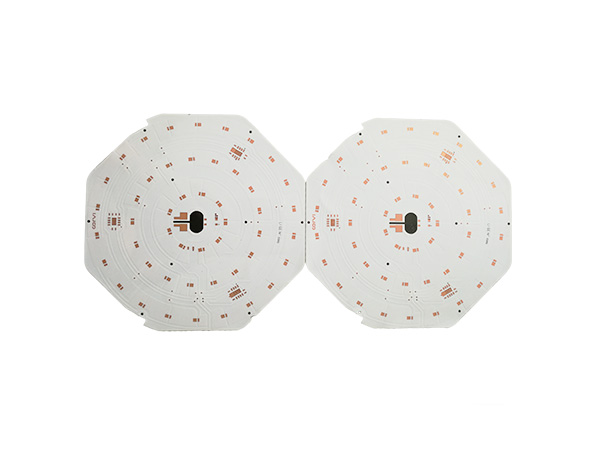

Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.
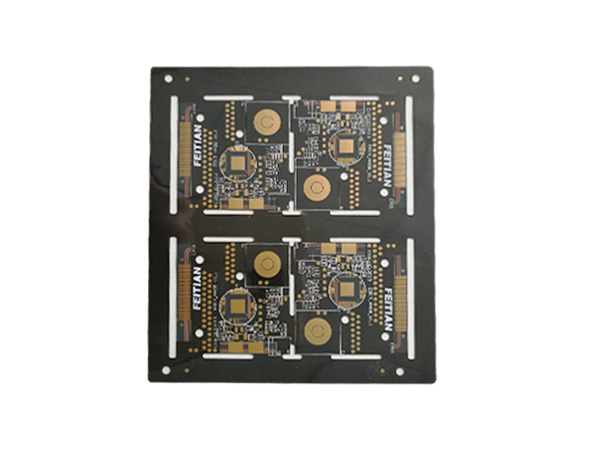

Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.

Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.
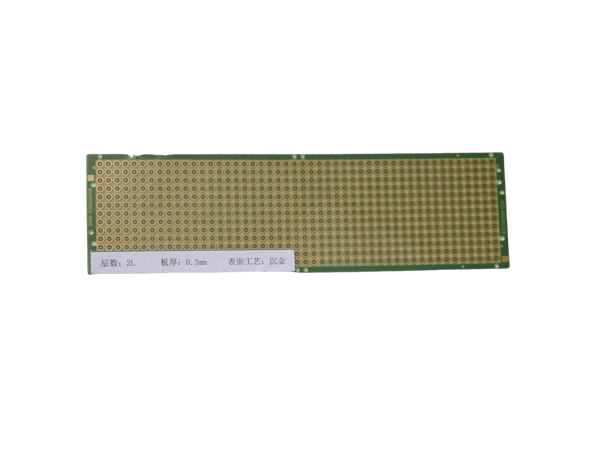

Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.
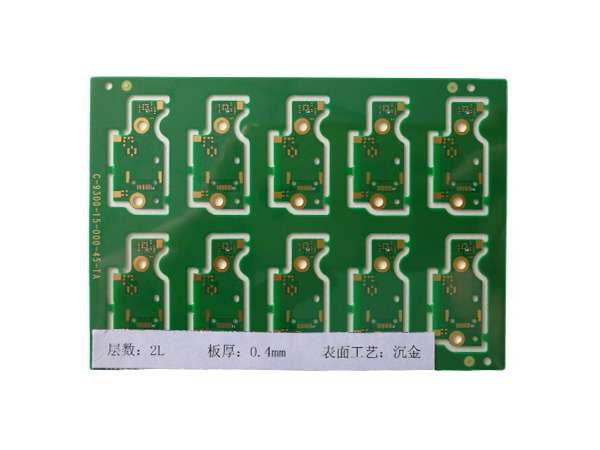
Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.
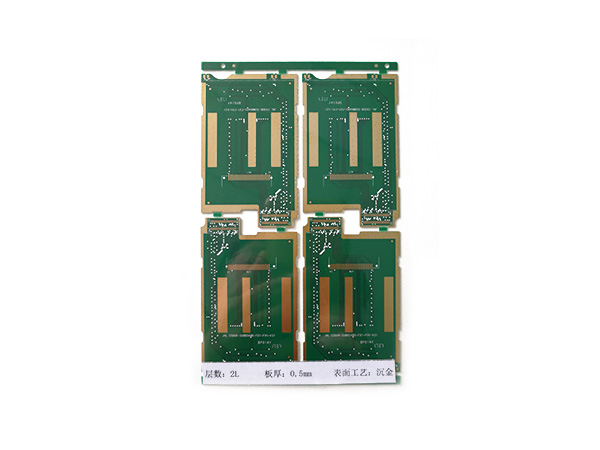

Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.
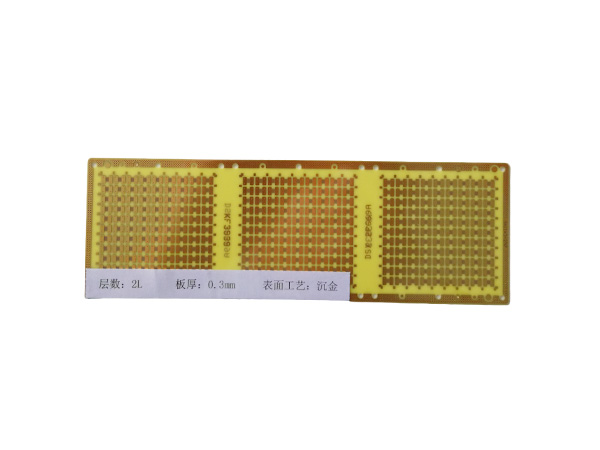
Ultrathin PCB is a type of circuit board specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements for space and weight in modern electronic devices. Its thickness is usually no more than 0.4mm, and some high-end products can be as thin as 0.05mm or even thinner. This characteristic makes it a key component for miniaturized electronic products, such as wearable devices, smartphones, medical implants, and so on.
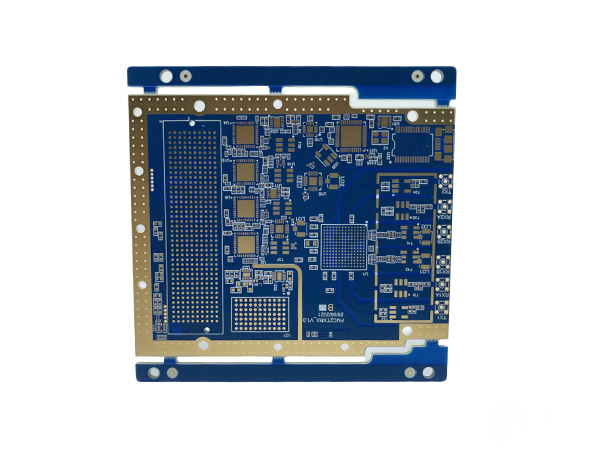
High Frequency PCBs are specialized printed circuit boards designed to handle and transmit high-frequency signals, typically operating above 1 GHz, with some applications extending into the millimeter-wave band (30 GHz and beyond). These boards are engineered to maintain signal integrity and reliability during high-speed data transmission, making them indispensable in modern high-speed communication and electronic syste
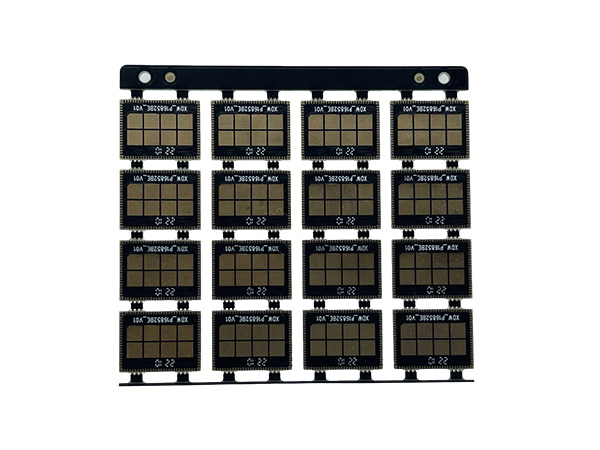
High Frequency PCBs are specialized printed circuit boards designed to handle and transmit high-frequency signals, typically operating above 1 GHz, with some applications extending into the millimeter-wave band (30 GHz and beyond). These boards are engineered to maintain signal integrity and reliability during high-speed data transmission, making them indispensable in modern high-speed communication and electronic systems.
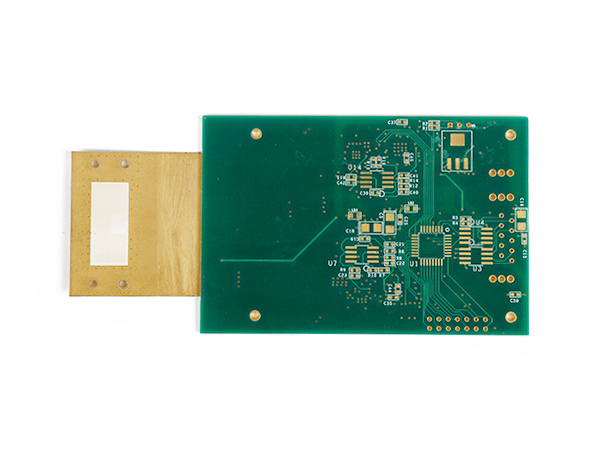
Product name: High frequency PCB
Material: Roger RO4350B + Shengyi S1000 FR4
Layers: 4layers
Copper: 1oz
Thickness: 1.20mm
Surface finishing: Immersion Gold 2U"
Soldermask: Taiyo Green soldermask
Application: communication device
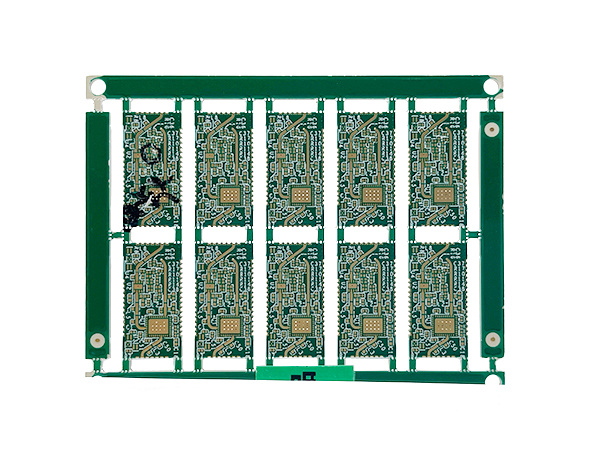
Product name: High frequency PCB
Material: Roger RO3003+TU872 SLK
Layers: 6layers
Copper: 1oz
Thickness: 1.60mm
Surface finishing: Immersion Gold 2U"
Soldermask: Taiyo Green soldermask
Application: communication modules
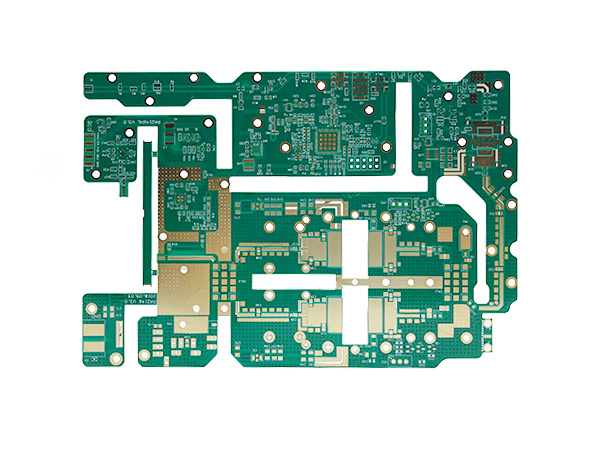
Product name: High frequency PCB
Material: Roger R4350B
Layers: 6layers
Copper: 1oz
Thickness: 0.25mm
Surface finishing: Immersion Gold 2U"
Soldermask: Taiyo Green soldermask
Application: communication main board
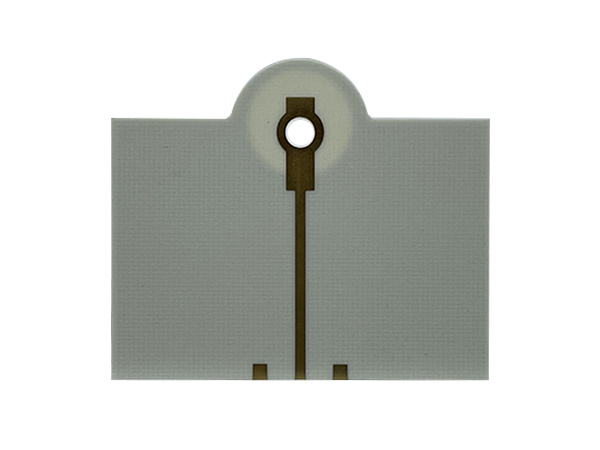

Product name: High frequency PCB
Material: Roger RO4350B
Layers: 2layers
Copper: 1oz
Thickness: 0.25mm
Surface finishing: Immersion Gold 2U"
Soldermask: White soldermask
Application: communication antenna
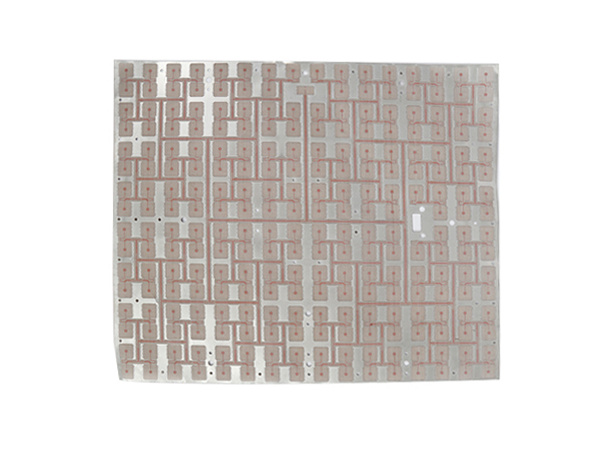
Product name: High frequency PCB
Material: TACONIC
Layers: 2layers
Copper: 1oz
Thickness: 0.20mm
Surface finishing: Immersion silver
Soldermask: transparent soldermask
Application: military industry
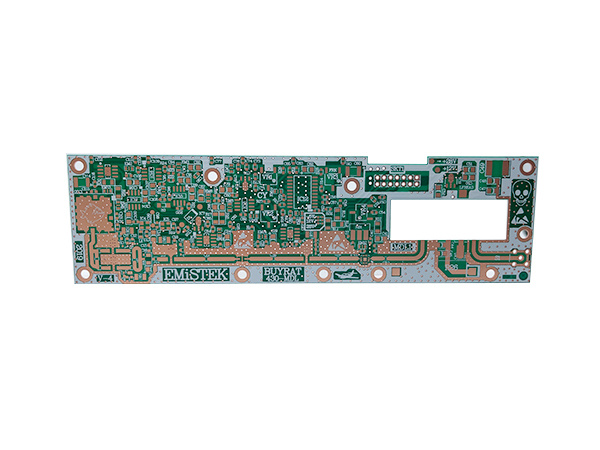
Product name: High frequency PCB
Material: Roger RO4350B
Layers: 2layers
Copper: 1oz
Thickness: 0.80mm
Surface finishing: Immersion Gold 2U"
Soldermask: Taiyo Green soldermask
Application: communication
Reach out to us via chat, phone, or our simple contact form.
Get a FREE Quote Today
Our business scope includes IC substrate design and simulation, IC substrate manufacturing, IC packaging and testing, as well as comprehensive hardware assembly services(PCB & PCBA).